Algorithm
[프로그래머스] 수식 최대화(2020 카카오 인턴십)
HONGNEW
2021. 1. 8. 22:12
프로그래머스에서 2020 카카오 인턴십 코테 출제 문제였던 수식 최대화 문제를 풀어보았습니다.
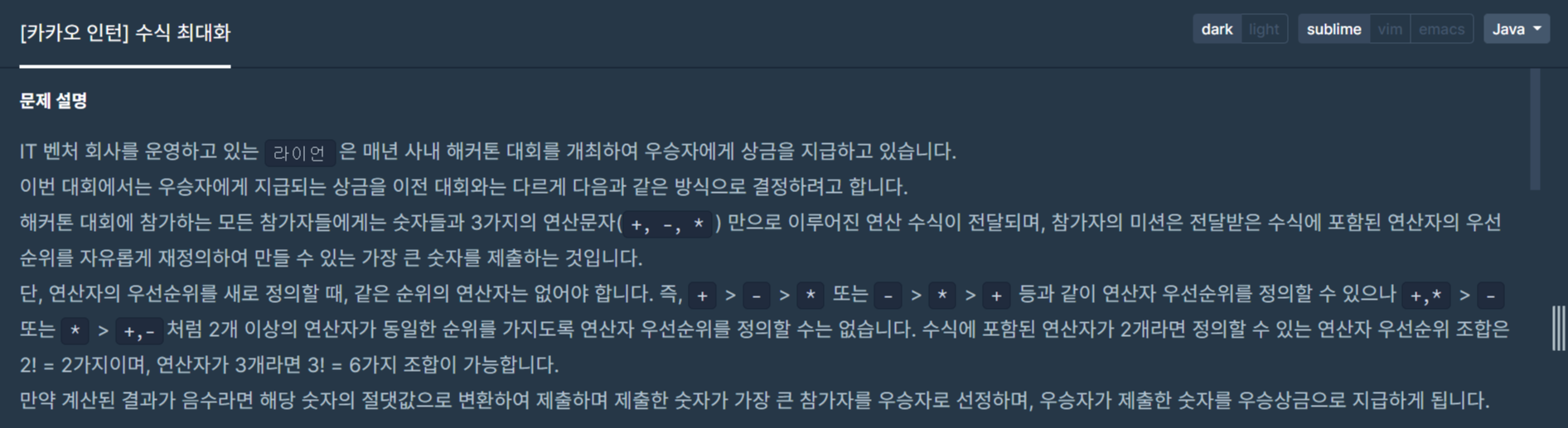
+, -, * 3가지의 연산자만을 포함하는 수식이 주어졌을 때, 연산자의 우선순위를 재정의하여 산출할 수 있는 가장 큰 수를 구하는 문제입니다.
이 문제를 풀기 위해서 고려해야 하는 사항은 다음과 같습니다.
1. 우선순위 조합 만들기
2. 순서에 따라 수식 계산하기
1. 우선순위 조합 만들기
우선순위의 조합은 순서가 있는 조합이므로 순열을 이용합니다.
n개 중 r개를 골라 순서가 있는 조합을 만드는 경우에는 아래 코드의 for 문을 n번, if 문에서의 depth조건을 r로 설정하면 됩니다.
이 문제의 경우에는 3개의 연산자 중 3개를 모두 사용해서 순서를 뽑으므로 3을 하드 코딩했습니다.
재귀 함수를 통해 모든 경우의 수를 찾아줍니다.
public void priorityPerm(char[] prioritys, boolean[] visited, int depth){
char[] operations = {'*','+','-'};
if(depth==3) {
for(int a=0; a<3; a++)
opPriority[cnt][a] = prioritys[a];
cnt++;
};
for(int i = 0; i<3; i++){
if(!visited[i]){
visited[i] = true;
prioritys[depth] = operations[i];
priorityPerm(prioritys, visited, depth+1);
visited[i] = false;
}
}
}
2. 순서에 따라 수식 계산하기
문제를 풀면서 가장 애먹었던 부분이 바로 이 부분이었습니다.
수식을 계산하는 부분을 어떻게 구현할까 한참을 고민하다가 후위 계산식으로 변환하여 처리했습니다.
주어진 수식을 연산자 우선순위를 반영하여 후위 계산식으로 변환하고, Stack을 이용해 수식을 계산해줍니다.
public long calOperation(String[] operations,char[] type){
Stack <String> priority = new <String> Stack();
Stack <Long> cal = new <Long> Stack();
HashMap <Character, Integer> hm = new <Character, Integer> HashMap();
ArrayList <String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
for(int a=0; a<type.length; a++){
System.out.println(type[a]);
hm.put(type[a], a+1);
}
for(int i=0; i<operations.length; i++){
if(operations[i].equals("*")||operations[i].equals("+")||operations[i].equals("-")){
while(!priority.isEmpty()&&hm.get(operations[i].charAt(0))>=hm.get(priority.peek().charAt(0))){
list.add(priority.pop());
}
priority.push(operations[i]);
}else{
list.add(operations[i]);
}
}
while(!priority.isEmpty()){
list.add(priority.pop());
}
for(int i=0; i<list.size(); i++){
System.out.println(list.get(i));
if(list.get(i).equals("*")){
long a = cal.pop();
long b = cal.pop();
cal.push(a*b);
}else if(list.get(i).equals("+")){
long a = cal.pop();
long b = cal.pop();
cal.push(a+b);
}else if(list.get(i).equals("-")){
long a = cal.pop();
long b = cal.pop();
cal.push(b-a);
}else {
cal.push(Long.parseLong(list.get(i)));
}
}
return cal.pop();
}
전체 코드
주어진 수식을 숫자와 연산자로 분리하는 부분이 깔끔하지 못해서 아쉽고, 수식에 포함되지 않는 연산자를 제외하는 등의 처리를 더 해주면 좋을 것 같습니다.
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
static char[][] opPriority = new char[6][3];
static int cnt;
public long solution(String expression) {
long answer = 0;
long maxResult = 0;
char[] prioritys = new char[3];
boolean[] visited = new boolean[3];
String temp = expression.replaceAll("\\+", "&+&");
temp = temp.replaceAll("\\-", "&-&");
temp = temp.replaceAll("\\*", "&*&");
String[] array = temp.split("&");
priorityPerm(prioritys, visited, 0);
for(int i=0; i<6;i++) {
maxResult = calOperation(array, opPriority[i]);
if(maxResult<0) maxResult *= -1;
answer = maxResult > answer ? maxResult : answer;
}
return answer;
}
public void priorityPerm(char[] prioritys, boolean[] visited, int depth){
char[] operations = {'*','+','-'};
if(depth==3) {
for(int a=0; a<3; a++)
opPriority[cnt][a] = prioritys[a];
cnt++;
};
for(int i = 0; i<3; i++){
if(!visited[i]){
visited[i] = true;
prioritys[depth] = operations[i];
priorityPerm(prioritys, visited, depth+1);
visited[i] = false;
}
}
}
public long calOperation(String[] operations,char[] type){
Stack <String> priority = new <String> Stack();
Stack <Long> cal = new <Long> Stack();
HashMap <Character, Integer> hm = new <Character, Integer> HashMap();
ArrayList <String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
for(int a=0; a<type.length; a++){
System.out.println(type[a]);
hm.put(type[a], a+1);
}
for(int i=0; i<operations.length; i++){
if(operations[i].equals("*")||operations[i].equals("+")||operations[i].equals("-")){
while(!priority.isEmpty()&&hm.get(operations[i].charAt(0))>=hm.get(priority.peek().charAt(0))){
list.add(priority.pop());
}
priority.push(operations[i]);
}else{
list.add(operations[i]);
}
}
while(!priority.isEmpty()){
list.add(priority.pop());
}
for(int i=0; i<list.size(); i++){
System.out.println(list.get(i));
if(list.get(i).equals("*")){
long a = cal.pop();
long b = cal.pop();
cal.push(a*b);
}else if(list.get(i).equals("+")){
long a = cal.pop();
long b = cal.pop();
cal.push(a+b);
}else if(list.get(i).equals("-")){
long a = cal.pop();
long b = cal.pop();
cal.push(b-a);
}else {
cal.push(Long.parseLong(list.get(i)));
}
}
return cal.pop();
}
}